Description
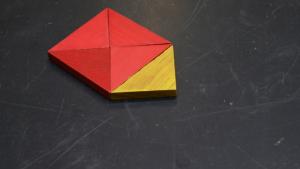
Five identical triangles can be arranged to show squares on each of the triangles sides, but one at a time. Demonstrating the Pythagorean Theorem involves showing the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle. By using geometric models or diagrams, students can see how the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This fundamental principle in geometry is crucial for understanding various mathematical concepts, including distance calculations, vector magnitudes, and trigonometric identities.
PIRA DCS Number
1A50.90A
Preparation & Instructions
1. Place the blocks on either the overhead projector.
2. Select the yellow triangle.
3. Along the hypotenuse of the yellow triangle arrange a square using four red triangles in a square so that their hypotenuses are pointing out.
4. Along the side arrange two red triangles in a square with the hypotenuses pointing inward.